TPM 2.0, Windows 11 PC health check, and the potential messy upgrade
This could get painful fast
Microsoft has finally, officially revealed Windows 11, and with that comes a barrage of information. And an equally large barrage of questions. One of the hottest topics right now is whether or not you can even get Windows 11 on your PC at all. On that, there is plenty of confusion.
There are a couple of details in particular that are adding to the confusion. One is the mention of TPM and the fact that you don't seem to be able to have Windows 11 without it. The other is that the app Microsoft offers to check if your PC is suitable for Windows 11 is throwing off what seem to be false negatives.
The second is most likely linked to the first. While we're a long way from Windows 11's expected release in October, it's clear already this could be a very messy upgrade path for a lot of Windows users. Here's what we know so far and what you might be able to do to prepare yourself ahead of time.
- Why Windows 11 could be the best OS for gaming
- Here's our pick of the best gaming laptops in 2021
- iMessage could now arrive to the new Microsoft Store
What is TPM 2.0?
TPM is the shorter name for Trusted Platform Module and it's essentially a security device for your PC. Microsoft describes it as such:
'Trusted Platform Module (TPM) technology is designed to provide hardware-based, security-related functions. A TPM chip is a secure crypto-processor that helps you with actions such as generating, storing, and limiting the use of cryptographic keys. Many TPMs include multiple physical security mechanisms to make it tamper-resistant, and malicious software is unable to tamper with the security functions of the TPM.'
Furthermore, TPM has been a requirement since 2016, so there's every chance your PC already has it. In some cases, it may be a physical module, in others, provided by the CPU. But for most recent PCs, this requirement shouldn't be an issue. The problems come in the form of making sure that TPM is enabled if you do have it. Because many PCs without a dedicated module will have it disabled by default.
It's this that is potentially going to cause the biggest pain point.
Get daily insight, inspiration and deals in your inbox
Get the hottest deals available in your inbox plus news, reviews, opinion, analysis and more from the TechRadar team.
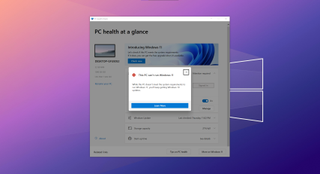
The Windows 11 PC health check app
To make figuring out whether your PC can run Windows 11 or not easier, Microsoft has the PC Health Check app (direct download). Install it, run the check, and it'll tell you whether you can get Windows 11. Easy!
Except it isn't.
The PC Health Check app is throwing a lot of false negatives, and the best bet is that it's TPM-related. We've seen PCs with a Ryzen 9 CPU and 32GB of RAM flagged as incompatible, while several years old Intel laptops are fine. Even on an Intel desktop, it failed until the TPM requirement was met.
If you have a hardware TPM module in your PC then you'll be fine, and several of the best laptops you can get will pass the test with flying colors. If you don't have a hardware module, this is where the upgrade process to Windows 11 could get messy.
- Here's our pick of the best laptops in 2021
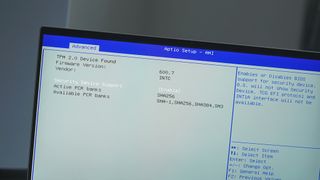
Enabling TPM and diving into BIOS settings
The good news is you probably have TPM and you can upgrade to Windows 11. At least, if you're using a PC built from 2016 on. The bad news is that unless you have a hardware module it won't be enabled and that means you have to go diving into your BIOS.
Millions and millions of people are about to have a WTF moment unless Microsoft somehow streamlines this or changes the requirements.
BIOS and UEFI menus aren't difficult to deal with, but if you've never looked at one it's a daunting prospect. And if you're not particularly computer savvy it can be terrifying. The first thing to do is make sure you have updated your BIOS to the latest version for your particular PC or motherboard.
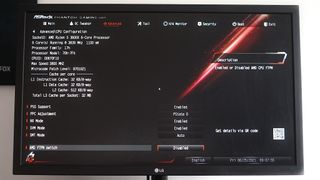
From there, you'll need to go into it when you start up your PC (usually with the DEL, F12 or F2 keys) and locate the TPM settings. This, again, will differ depending on your motherboard and whether you're using Intel or AMD. On AMD, you'll be looking for a setting called 'AMD fTPM' to enable, while on Intel it may be labeled something like 'Intel Platform Trust Technology'.
While you're in your BIOS you'll also need to enable Secure Boot, which most likely lives on the 'Security' tab. This is another requirement of Windows 11, and while it may have consequences for dual-boot Windows and Linux systems, that's another tale entirely. If you want Windows 11 these two things must be enabled as it stands.
Buying a hardware TPM module
Hardware TPM modules are ultimately better than the firmware-based solutions from AMD and Intel, but if you built your own PC you most likely didn't include one on your shopping list. The good news is, as long as your motherboard has a header for one, they're not expensive and easy to fit.
Exact details can be found in the manual for your motherboard, but the module itself will just attach to some header pins and won't require any additional power. As for price, you're looking at as little as £10/$10 for a TPM 2.0 module, or up to £30/$30 depending on the manufacturer.
You might not need one though, so definitely check whether you have a firmware-based solution before buying anything.
Summary
The good news is that the TPM 2.0 requirement might not be the barrier you think it is, and even if the app is telling you that you're not eligible for Windows 11, you might well be.
The issue is that this is a massive pain point to upgrading successfully and it's involving aspects of a PC that millions of average PC users will have no knowledge of. As it stands, this could be the messiest upgrade yet.
But, follow the steps we outlined here and you will at least know for sure where you stand well in advance. We can only hope Microsoft steps in and streamlines it some more.
- Windows 11: Everything we know so far
